Digital dental X-rays are more efficient and safer than traditional film-printed X-rays. Although conventional dental X-rays today predict low radiation levels, digital dental X-rays produce up to 90% less radiation than others. Our practice is at the forefront of technology, and we use state-of-the-art equipment to protect patients during diagnostic procedures.
What are the benefits of digital dental radiology?
The advantages of digital radiology are numerous:
It subjects the patient to minimal irradiation compared to conventional radiology.
Once the digital image is on the screen, it is possible, if necessary, to adjust it by enlarging the areas that require close inspection.
Identifying small lesions or other areas of interest is much easier and faster without waiting to develop an X-ray film.
Another advantage is the ease with which you can view these images on a screen to explain the problems to the patient and what is the best way to treat them.
Easy transfer: Digital images can eventually be sent by e-mail to other specialists with a much faster and more efficient process than sending conventional X-ray films or photographs of analog X-rays.
Digital X-rays are environmentally friendly because there is no need for film and acids to create and reproduce copies of them.
During the first specialist visit, the dentist can only see the superficial part of the teeth and no other essential parts of the mouth hidden from view, including the roots of the teeth, the areas of contact between the teeth, the supporting alveolar bone, any infections, etc. Digital X-rays allow you to see areas hidden from view in great detail, making them indispensable for formulating a correct diagnosis and elaborating the treatment plan suitable for the individual patient.
Caries, for example, can develop in the areas of contact between the teeth, areas difficult to access, hidden from both the view of the patient and the dentist.
Digital radiographs show the internal and surrounding structures of the tooth and allow early identification of carious lesions and any signs of infection.
How often do you repeat dental X-rays?
The exact frequency to repeat the radiographic examination will depend on the patient’s dental health status and medical history. The dentist will suggest when to do them and how often to repeat them to check your health.
Are digital dental X-rays safe?
Digital dental X-rays are so safe that even pregnant women can receive digital X-rays in a dental emergency. At the same time, it is good practice to delay the execution of conventional X-rays until after the baby’s birth. In addition, digital sensors have protective single-use plastic barriers for each patient to eliminate the possibility of cross-contamination and infection.
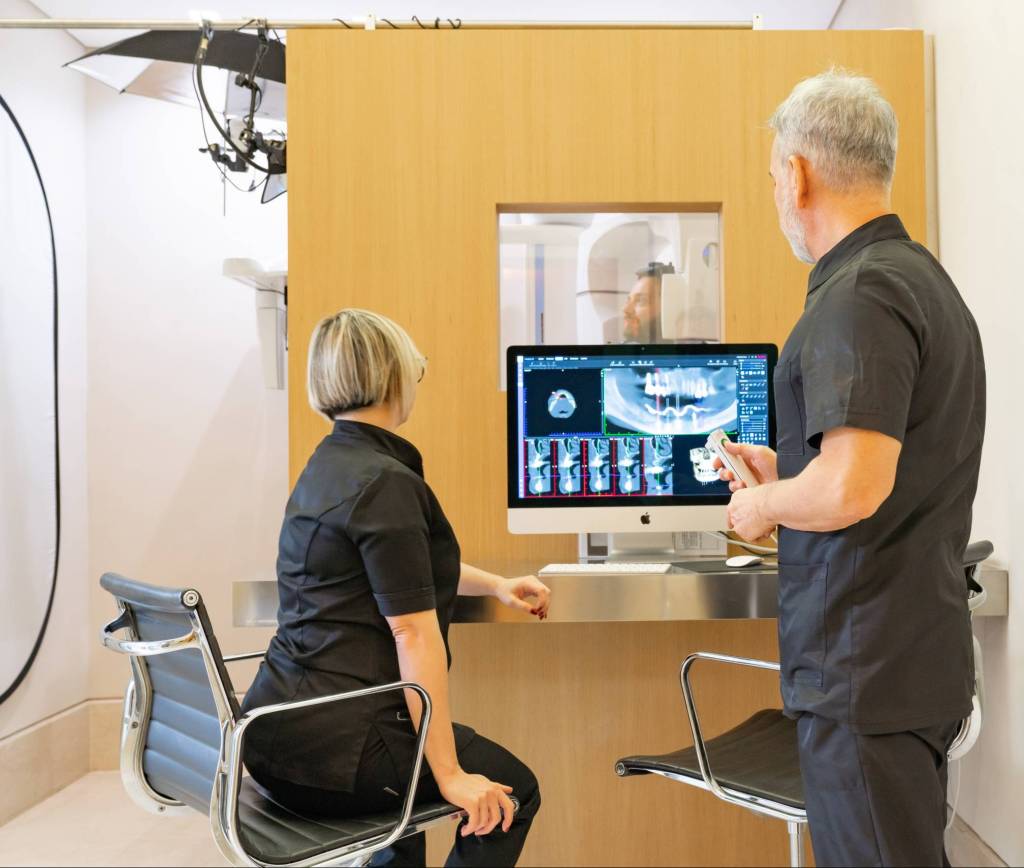
Digital dental radiology: endo-oral X-ray, TMJ CBCT and CBCT
Digital dental radiographs can be intraoral or extraoral.
RX ENDORAL
Intra-oral digital dental radiographs are the most frequently used radiographs. They provide a vast amount of data not available by any other means, both on the condition of the teeth and on the supporting alveolar bone.
The main types of endo-oral radiographs are:
they are used to detect interproximal caries (in the area of contact between adjacent teeth) to check the condition of the bone around the teeth and to assess the fit and integrity of dental restorations, including crowns and fillings.
periapical X-ray shows the entire tooth from its crown to the apex of the root and the alveolar bone surrounding and supporting the tooth. Periapical X-rays help detect caries and dental infections and evaluate the possible bone loss around the teeth that may occur in case of periodontal disease.
EXTRAORAL RX
Main types of extra-oral radiographs:
orthopanoramic radiography is performed by an X-ray that rotates around the head, providing a single two-dimensional image of all teeth in the upper and lower arch and bone structures. Panoramic radiographs have only an indicative function for a first screening, which needs to be deepened with further examinations. Panoramic X-rays help evaluate wisdom teeth, including cysts or infections and other jaw problems, and for planning orthodontic treatments.
the two-dimensional skull radiography in the anteroposterior and latero-lateral projection is essential to elaborate the orthodontic treatment plan.
it is performed with a radio diagnostic device that rotates around the head and provides a three-dimensional scan of dental and bone structures. This investigation is essential for dental diagnosis and surgical and implant planning.