What is dental diagnostics?
The term TMJ dysfunction, describes a group of clinical symptoms related to masticatory muscles, temporomandibular joints, and associated structures.
When the upper and lower jaws do not match the ideal position, it is called “malocclusion”. Malocclusions can cause craniomandibular disorders or be a contributing factor.
Some symptoms associated with craniomandibular dysfunction are:
Headache / migraine
Tinnitus / noises in the ears
Pain in the back, shoulders, and neck
Spinal and joint problems
Pain in the face
Pain in the mandibular joint and surrounding regions, including the ear
Inability to open your mouth without problems
Sounds similar to a click, pop, or rubbing at the level of the mandibular joint
Blockage of the jaw when trying to open the mouth
Discomfort or a strange feeling when chewing
Swelling in the side of the face, neck, or shoulder
Reduced hearing
Dizziness
Visual problems
Bruxism (teeth grinding)
Clenching (static clenching of teeth)
Correlations between the masticatory system and other structures
Our masticatory system is related to a large group of anatomical structures, including:
Skull
Cervical spine
The auditory and balance system
Postural system
The fascial neuro system.
The sight
A malocclusion can alter these structures’ functions and give rise to disorders in the neck area, the masticatory muscles, or other districts.
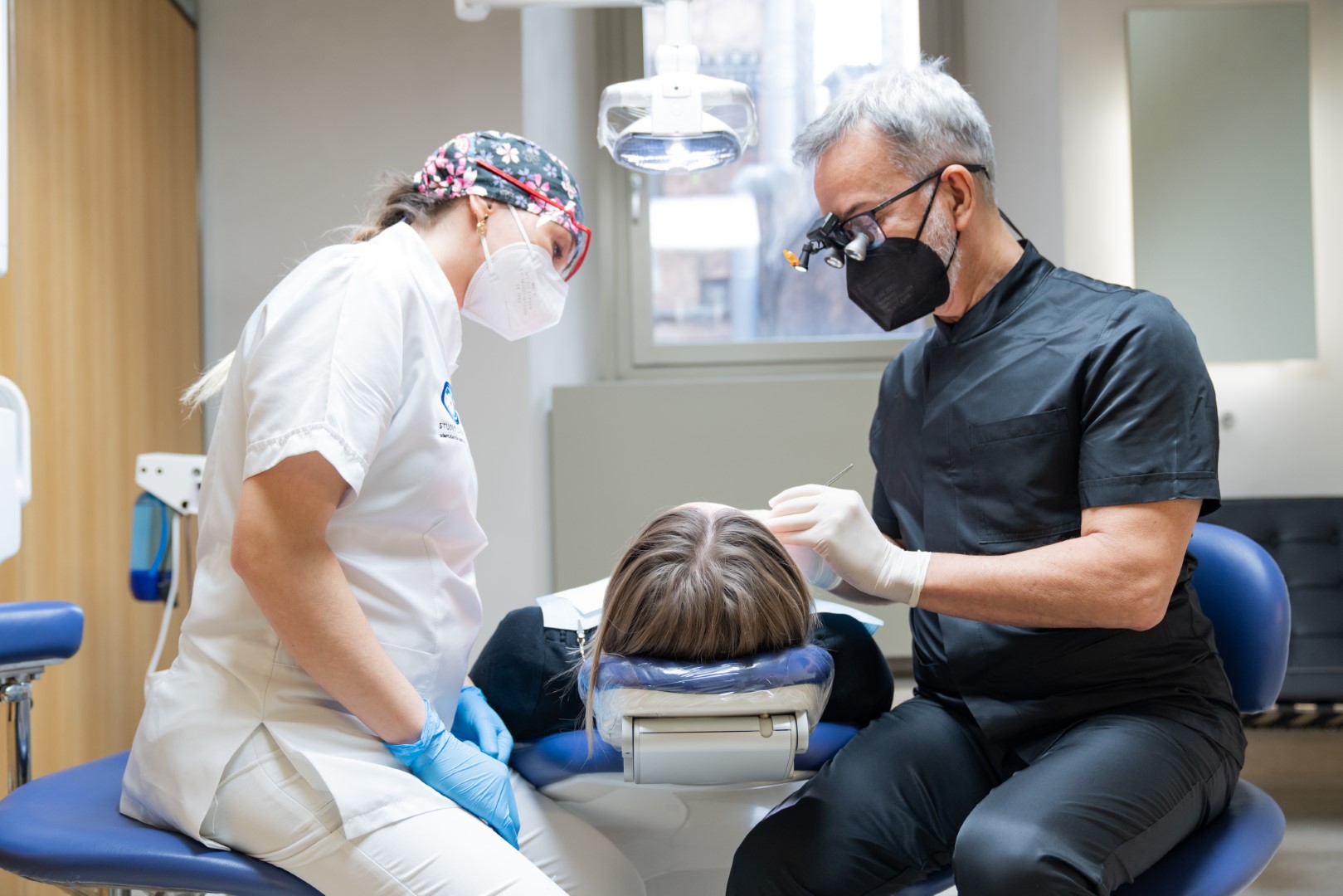
The specialist visit
In the presence of symptoms, a specialist examination is advisable to examine the temporomandibular joints, the masticatory muscles, and the existing cranio-mandibular relationships. During the diagnostic visit, the specialist will ask for details about the patient’s problems and conduct a clinical and instrumental examination of his stomatognathic system. Based on the results of the visit, the patient will receive a diagnosis and a treatment plan.
Initial therapy
In some cases, the initial therapy will consist of an occlusal plaque (generically called bite) used to induce muscle relaxation and rediscover and test the correct cranio-mandibular relationship. It should be emphasized that there are occlusal plates of different types from which it is necessary to select the one indicated to the specific clinical case.
These devices can induce a significant improvement in muscle contractures and remission or disappearance of pain even after a short period of use.
Stabilization therapy
After the pain has disappeared, further orthodontic or restorative treatment may be required to ensure long-term treatment success.
Sometimes, the dentist must work with other specialists to treat the causes and symptoms therapeutically and simultaneously.
Early diagnosis
The most effective strategies in medicine are prevention and early diagnosis.
Regular visits will allow the specialist to make an early diagnosis, avoiding worsening your symptoms and the onset of pain.